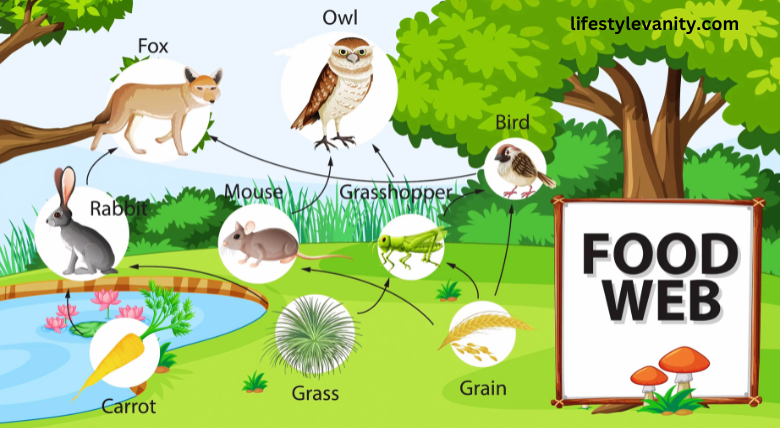
Total Direct to Comprehending the Food Web
Overview
The nourishment web A more complex frame of the nourishment chain is one of the most interesting thoughts in the environment. The food web highlights the interconnecting of distinctive species by enlightening the various channels through which vitality and supplements pass through an ecosystem.
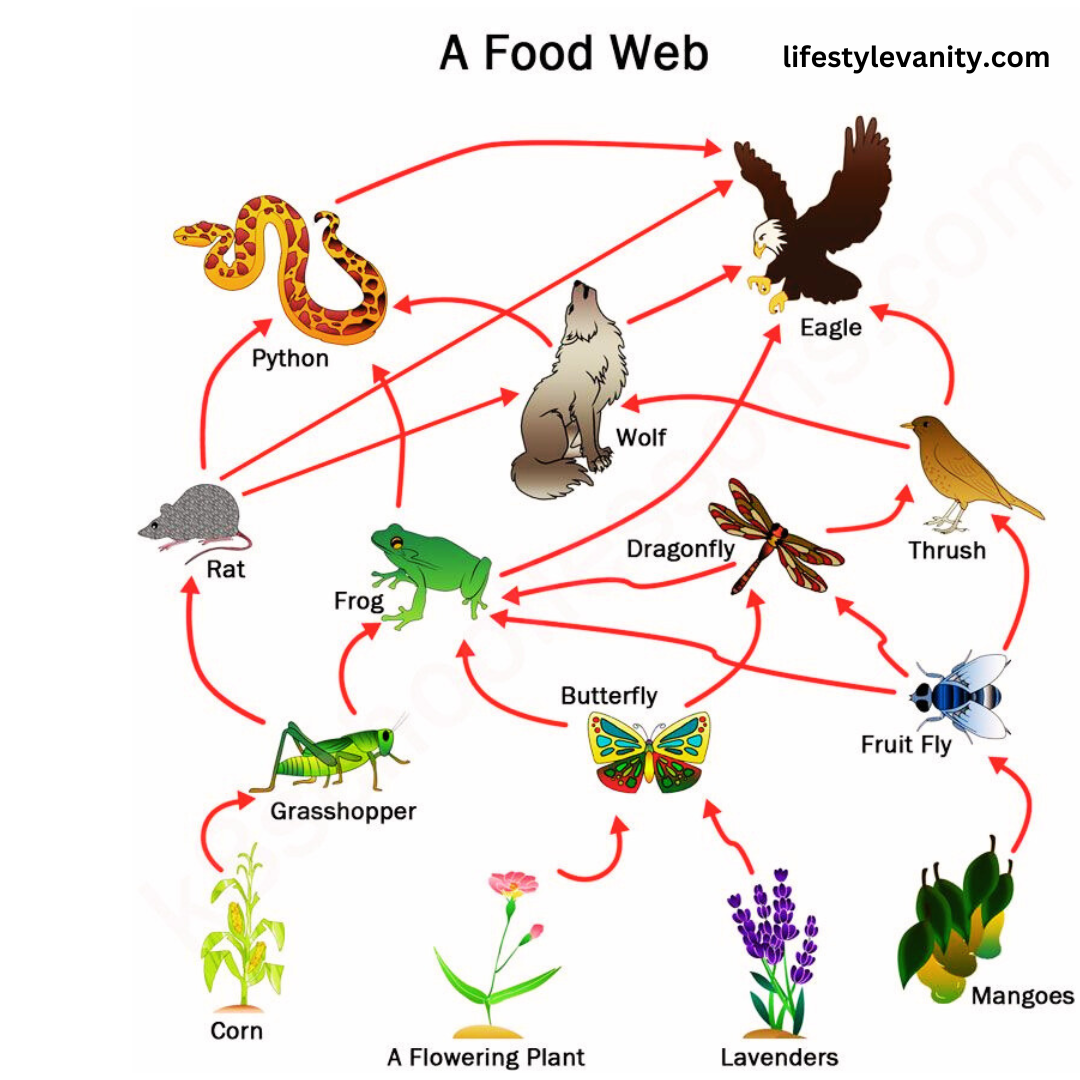
Food web: what is it?
An arrangement of interconnected food chains is called a “food web.”It traces the affiliations between distinctive species in a natural framework as a result of their feeding associations. With a single straight imperative streamway, the food web joins a grouping of pathways.
Food Web Components:
Makers / Autotrophs: Makers are the establishment of the food web. These are plants and green growth that utilize photosynthesis to make their food by changing solar energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Customers
Heterotrophs, or customers, depend on other animals for food. They drop into three essential categories:
Primary Buyers: Producer-eating herbivores (deer, rabbits, etc.).
Tertiary Customers: Falcons and lions are cases of summit predators that nourish auxiliary consumers.
They are destructive
Taking care of weeds and endless ecosystems, they disperse debris and dead bacteria and recycle supplemental nutrients back into the environment.
The critical stream in the food wing is unidirectional, starting with producers and creating disturbing and securing products in a variety of applications. 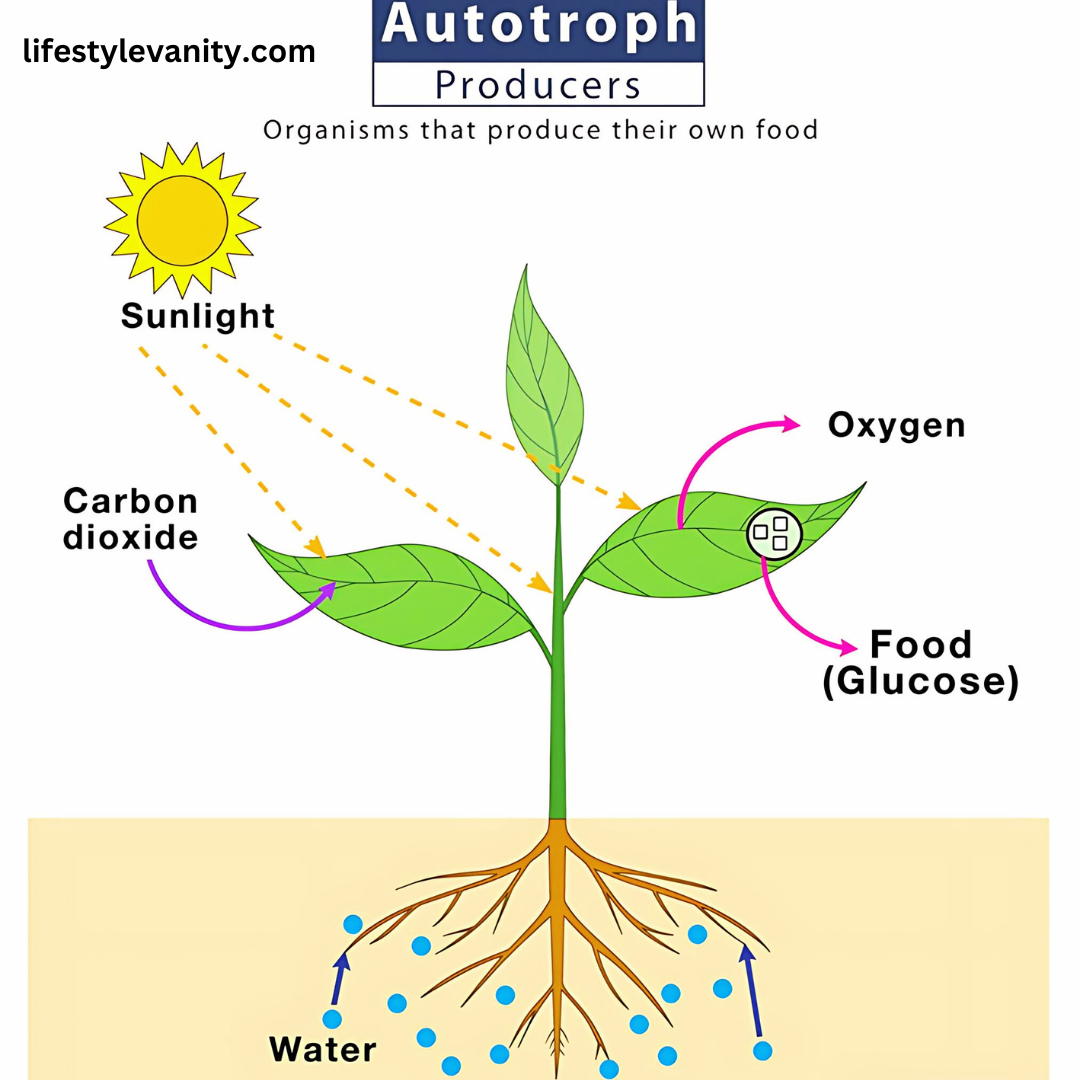
Food Web Types
Grazing Food Chains
They are predicated on herbivores expending on living plants, anywhere they are in this way expended by carnivores. Earthbound situations habitually have touching food webs.
Detrimental Food Chains
This concentrates on the natural matter breakdown after death.
The Esteem of Food Chains
Understanding food networks is fundamental to comprehending biodiversity and natural flow. They clarify the perplexing connections between species and help biologists determine the potential impacts of changes in one populace on others.
The Impact of People on Food Webs
Food networks are enormously affected by human activities, including pollution, overfishing, and deforestation. These exercises can potentially disturb natural equalizations, which may cause a species’ decay or termination.
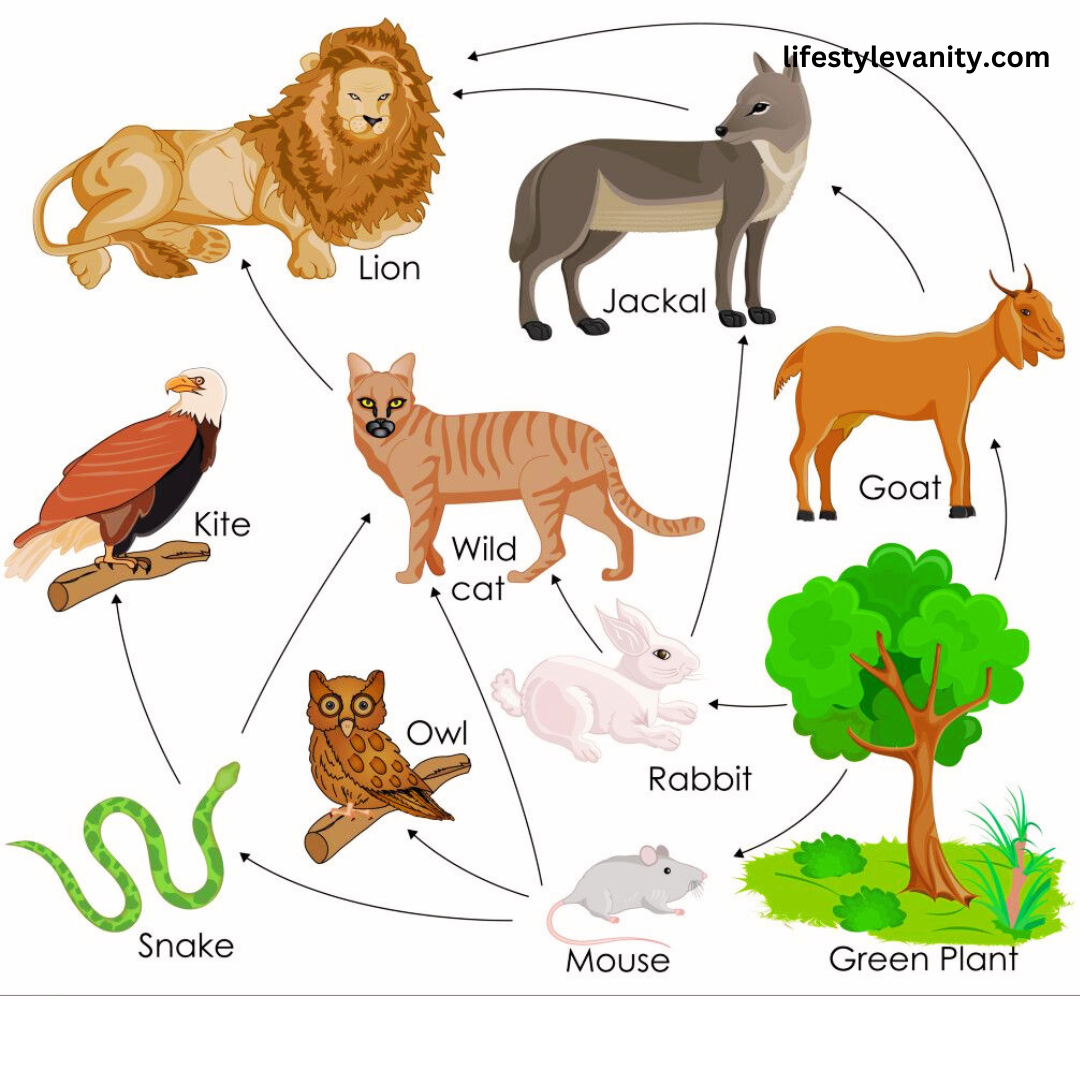
Case Studies
The Wolves of Yellowstone
The reintroduction of wolves to Yellowstone National Park best outlines the revamping of the food web.
Elk overpopulation came about from the early 20th century destruction of wolves from the stop.
Ecosystems of Coral Reefs
Among the planet’s most differentiated biological systems, coral reefs have complex food networks domestic to various species. they are amazingly vulnerable to harm caused by people, like contamination and climate change. Impressive changes in the food chain brought almost by the termination of cornerstone species, huge savage angles, or coral itself, can result in a drop in biodiversity.
Conclusion
Understanding food networks is pivotal to comprehending the complexity and interdependency of environments. Scientists can learn about the solidness and well-being of biological systems and the impacts of human movement by inquiring about food networks. It is basic to defend these complex systems to maintain biodiversity and ensure the strength of characteristic ecosystems. The centrality of preservation endeavors is highlighted by information about and appreciation for the delicate harmony inside food networks.